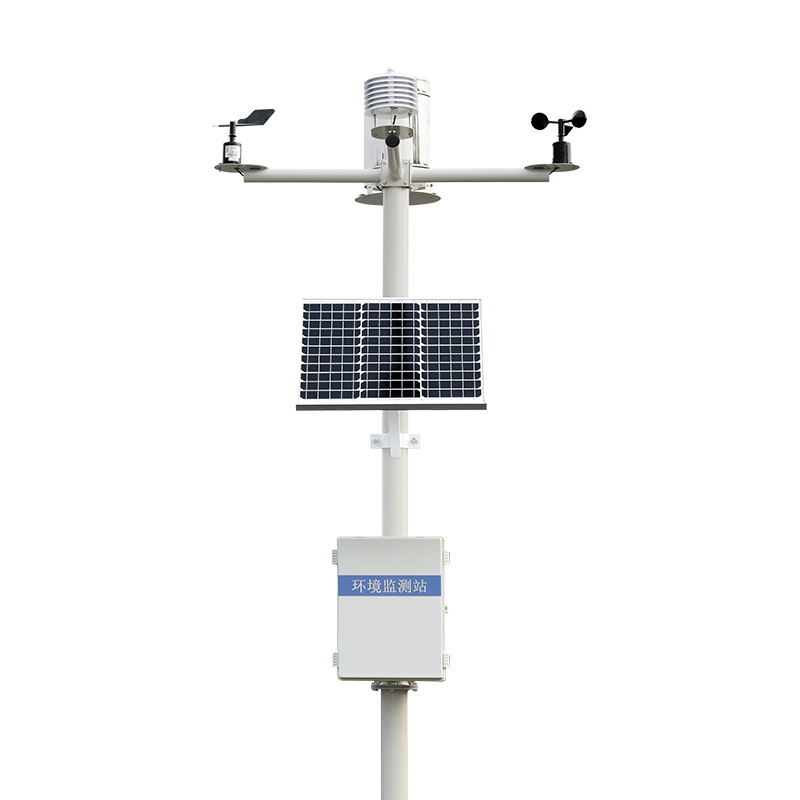
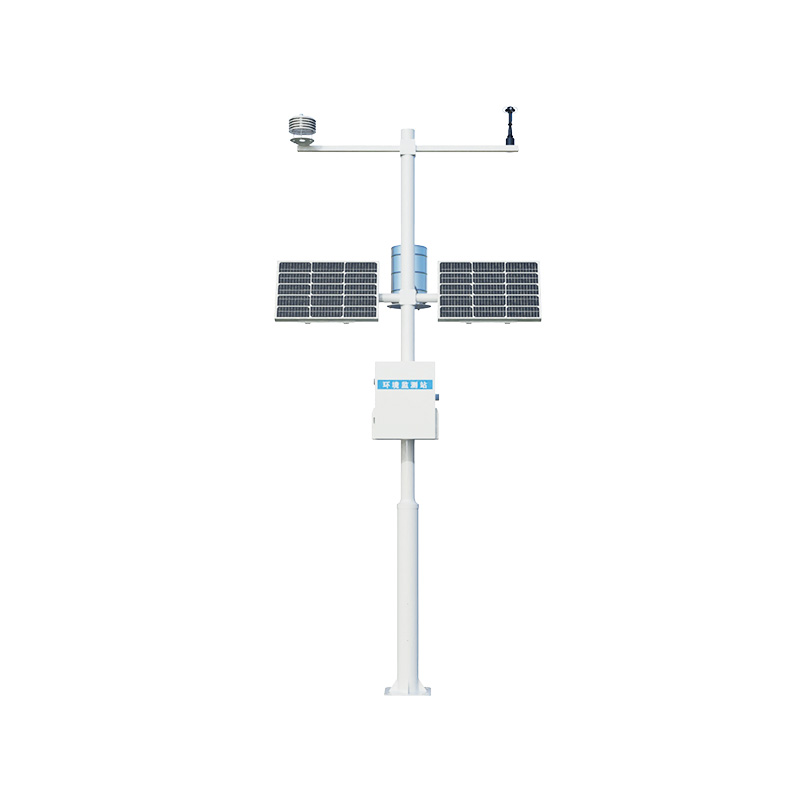
In forest parks, abundant vegetation and fresh air often generate a large number of negative oxygen ions. These negative oxygen ions not only help purify the air and improve the breathing environment, but also promote human metabolism and enhance immunity. Therefore, monitoring the content of negative oxygen ions in forest parks is not only a direct reflection of environmental quality, but also an important means to protect the ecological environment and promote human health. The negative oxygen ion monitoring system, through advanced sensing technology and data processing algorithms, can monitor the content of negative oxygen ions in forest parks in real time.
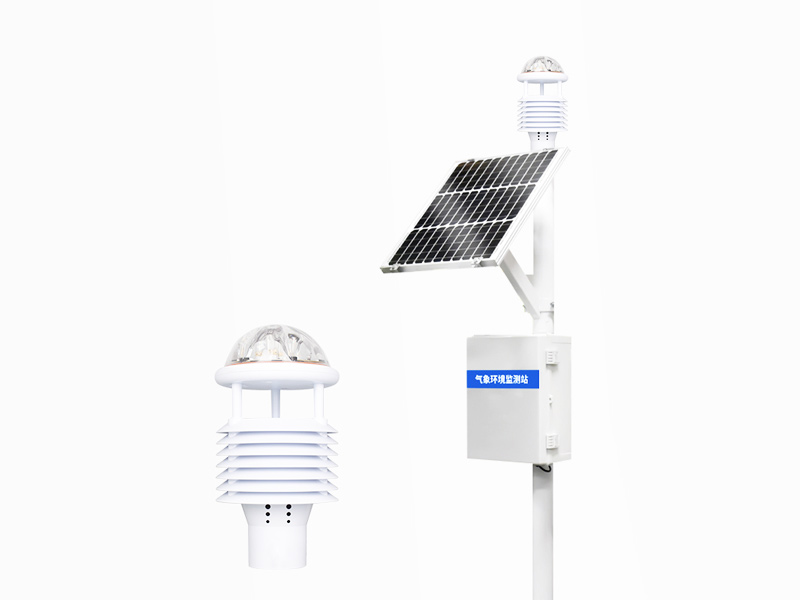
The WX-FZ5 Forest Park negative oxygen ion monitoring system uses sensors to capture the signals of negative oxygen ions in the air, and conducts calculations and analyses through internal algorithms, ultimately obtaining accurate data on the concentration of negative oxygen ions. These data will be transmitted in real time to the monitoring center to provide decision support for managers.
On the one hand, these data can serve as important indicators for evaluating the environmental quality of forest parks, providing scientific basis for managers to take timely measures to improve the environmental quality. On the other hand, monitoring data can also be used to study the correlation between negative oxygen ions and the ecological environment as well as human health, providing strong support for environmental protection and human health research.
By making monitoring data public and holding popular science activities, the public can have a more intuitive understanding of the environmental quality in the forest park, and enhance their awareness and sense of responsibility for environmental protection. Meanwhile, the application of the monitoring system can also inspire the public's love and awareness of protecting the natural environment, and promote the formation of a favorable atmosphere where the whole society participates in environmental protection together.

Article address:
http://www.0757gl.com/en/newcen/1478.html


















 Home
Home phone
phone Product Overview
Product Overview Contact Us
Contact Us